Author: Huatai futures engineer Chen Mu Asaruo
First, the first half of the market summary
In the first half of the year, due to the conflict between Russia and Ukraine, repeated epidemics in many places in China, and tightening macro liquidity, the overall price of zinc showed a trend of rising first and then declining. From January to mid-April, refineries that had previously cut production in Europe were still plagued by high power costs. The outbreak of the conflict between Russia and Ukraine in late February and the sanctions imposed on Russia by Europe and the United States made the market more worried about energy shortage. The high fluctuation of energy prices keeps the worries about the shortage of refined zinc supply in Europe fermenting. In addition, the violent fluctuation of nickel in mid-March drove the price of zinc up. Zinc alloy climbed from $3,524.5/ton at the beginning of the year to $4,513/ton, once hitting an all-time high of $4,896/ton, with an increase of over 28%. However, as the demand for natural gas entered the off-season, the PMI data of manufacturing industries in major economies in the world peaked, and the Fed’s interest rate hike was radical, the market’s expectation of global demand turned pessimistic, and Lunzinc entered the downward channel. Under the impact of multiple negative macro, the gains of the previous round were retreated. The trend of Shanghai zinc and Lunzinc is similar, but in the rising and falling market, the increase and decrease are not as good as Lunzinc. In the first half of the year, due to the environmental protection control of the Winter Olympics and the outbreak of many domestic epidemics, the demand was weak. However, in the early stage of the epidemic, the market’s expectation of post-epidemic consumption recovery was more positive, which was supported by Shanghai Zinc. However, due to macro pressure, the market began to worry that the economy will fall into recession in May, and the price of zinc was under pressure.
Second, the prospect of zinc market in the second half of the year
From a fundamental point of view, zinc will be a relatively strong variety in the second half of the year. However, the unilateral market is still subject to the macroeconomic situation and the impact of domestic infrastructure.
Macroscopically, after the Federal Reserve raised interest rates by 75 basis points in June, the inflation rate is still at a high level. The tightening of overseas liquidity has caused concern about the global economic recession. The changes in economic data in the second half of the year and the adjustment of Fed policies will change the market’s expectations of the economic recession, so it is necessary to pay attention to the impact of macroeconomic performance on zinc prices in the future.
Overseas, the energy risks brought by geopolitics will continue in the second half of the year, and European smelters will be difficult to resume production in the short term due to high cost pressure. On the demand side, due to the dual pressures of tight liquidity and high inflation, it is expected that overseas demand will fall under pressure in the second half of the year. At present, the problem of low overseas inventory still exists, and the global total inventory of LME zinc ingots is at a historical low. Under the background of low inventory and high fluctuation of energy prices, the market is still relatively pessimistic about the subsequent overseas zinc ingot supply, and the soft-forced market may still be staged repeatedly, and the price of zinc is supported to some extent. It is necessary to pay attention to the short-term fluctuation interference of prices caused by unexpected reduction of supply side and sudden increase of cancelled warehouse receipts.
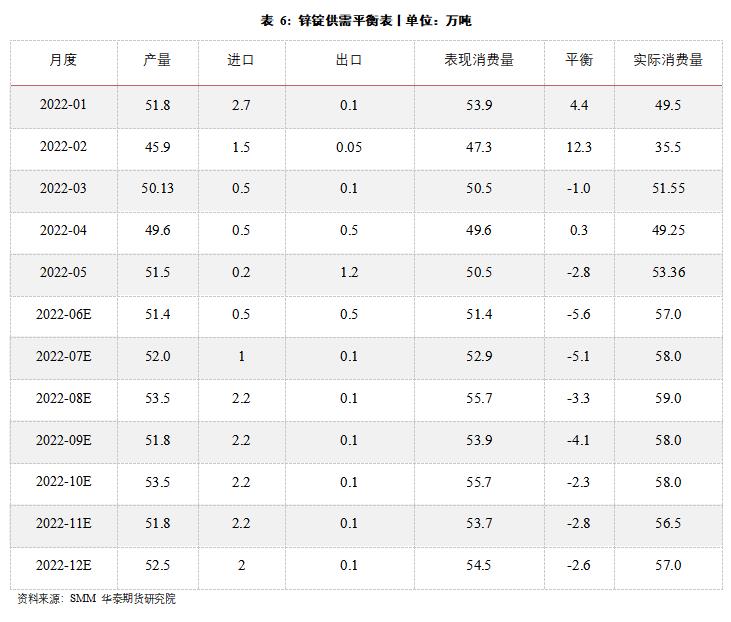
On the domestic supply and demand side, considering the slow resumption of work in domestic mines and the difficulty in increasing production due to factors such as the decline in ore grade, and the inflow of imported ore still takes some time, it is expected that the supply of raw materials in domestic smelters will be relatively limited in the second half of the year, and the processing fee may be further lowered. In addition, the production of some refineries in Guangxi was temporarily interrupted by heavy rain recently. It is estimated that the domestic refined zinc output will be around 6.15 million tons during the year, with a year-on-year increase of 0.5%. In terms of import and export, considering the slow recovery of the Hulun ratio, there may be a chance to change from net export to net import in the second half of the year. However, due to the slowdown of overseas consumption and the limited recovery of domestic consumption, it is expected that the import and export window will be difficult to open continuously. It is estimated that the annual net import will be 115,000 tons, a decrease of 355,000 tons compared with last year. From the perspective of terminal consumption, it is expected that zinc consumption will increase in the second half of the year, among which infrastructure and automobile sectors will contribute the main increase in zinc consumption, while real estate and household appliances are relatively dull. Due to the strong infrastructure nature of zinc demand, there is room for domestic demand to repair in the second half of the year. However, considering that the consumption affected by the impact of the epidemic in the first half of the year may be difficult to make up, the primary consumption continues to be sluggish, and the global demand is weakening, the overall growth rate of consumption is lowered to about -7% in a relatively pessimistic situation, with an annual consumption of 6.37 million tons and a supply gap of about 105,000 tons. If there are obvious signs of stimulating recovery in terminal sectors such as infrastructure, the supply gap may be further enlarged.
At present, the global zinc ingot inventory level is still at a low level, and the profit margin of zinc smelters at home and abroad is relatively limited. Compared with other non-ferrous metals, zinc may be relatively resistant to falling. In the second half of the year, it is estimated that Shanghai Zinc will have some support between 19,000-20,000 yuan/ton. Considering the fundamental support and the high elasticity after macro-stabilization, it is recommended to allocate more zinc in cross-variety allocation, but we should pay attention to the impact of macro risks on prices.
Third, the supply side situation
(A) the output of overseas mines is less than expected.
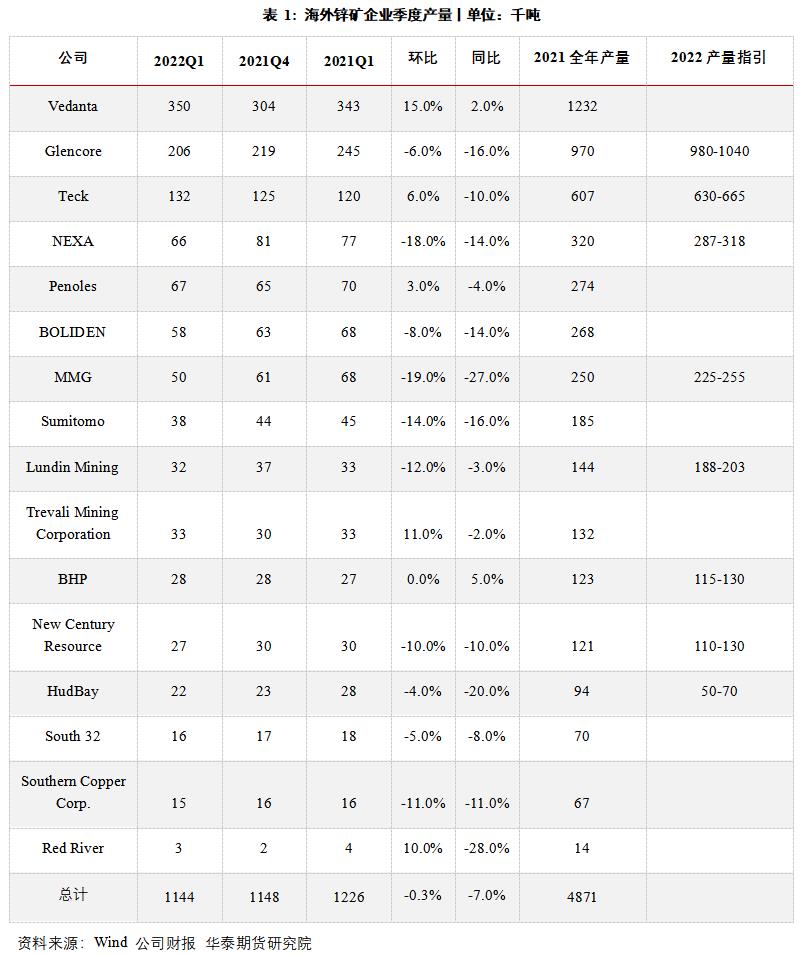
Judging from the financial report of overseas zinc mine enterprises in the first quarter, although the output of overseas zinc concentrate rebounded significantly in 2021, the pace of recovery has gradually slowed down since the second half of the year. In Q1, 2022, the output of overseas zinc concentrate showed a negative growth year-on-year, and the planned new output of 135,000 tons decreased compared with the planned increase of 216,000 tons at the end of last year. The main reasons are: 1) the increase in employee absenteeism caused by the COVID-19 outbreak, which led to the shortage of labor in some mining enterprises, such as Dugald River;; 2) Some mines stopped production due to heavy rainfall, such as Vazante and Antamina;; 3) Judging from the ore grade in recent years, the continuous decline in the grade of some mines has led to a decrease in output, such as Rosebery.
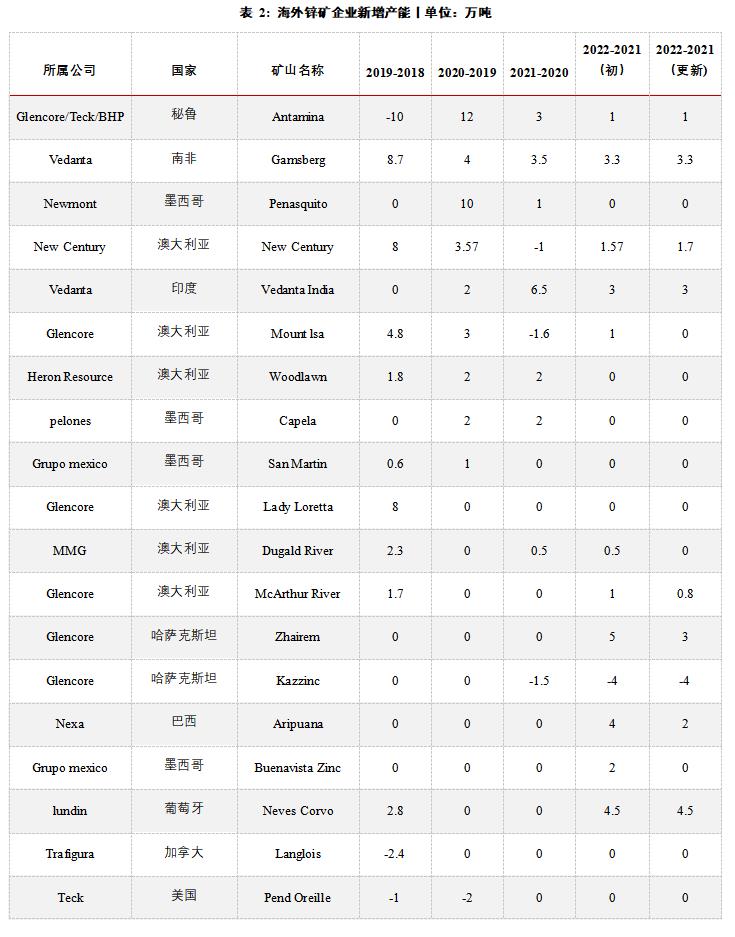
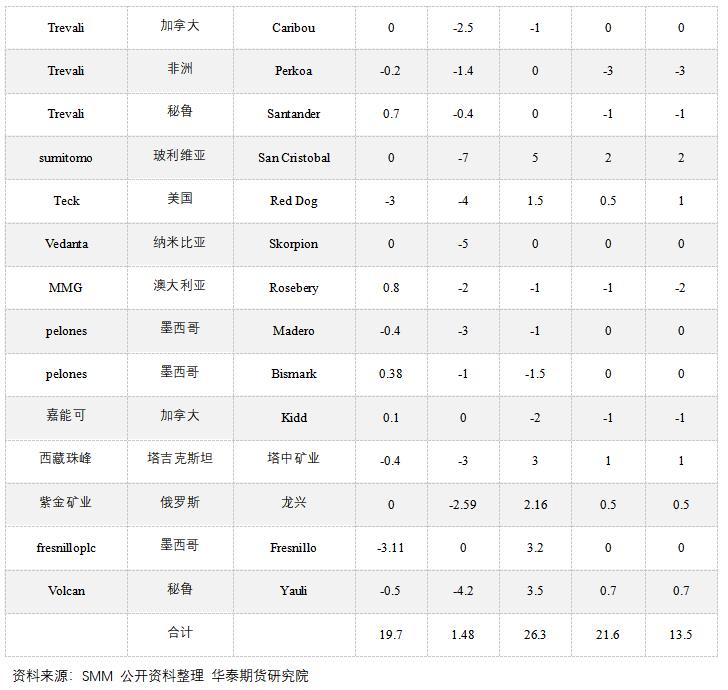
Combined with the production guideline and capital expenditure budget of enterprises in 2022, it is found that most mining enterprises have not increased the scale of capital expenditure of zinc mine business, and under the situation of tight capacity expansion, some mining enterprises have lowered their production targets in 2022 to varying degrees based on the gradual reduction of ore grade and the future shutdown plan. Therefore, it is expected that the current round of zinc mine capacity expansion cycle is coming to an end, and the increase in overseas mine supply will be less than market expectations during the year.
Although the output and increment of overseas zinc mines were less than expected, in the first half of 2022, the continuous high energy prices in Europe affected the production of local smelters, and the historical price difference between domestic zinc concentrates and imported concentrates in China also kept China buyers away from the imported spot market, which eased the tension in overseas zinc concentrate market. If the subsequent energy crisis is alleviated, smelting enterprises will resume production one after another, and the shortage of mine ends will be enlarged.
(B) domestic ore supply is tight.
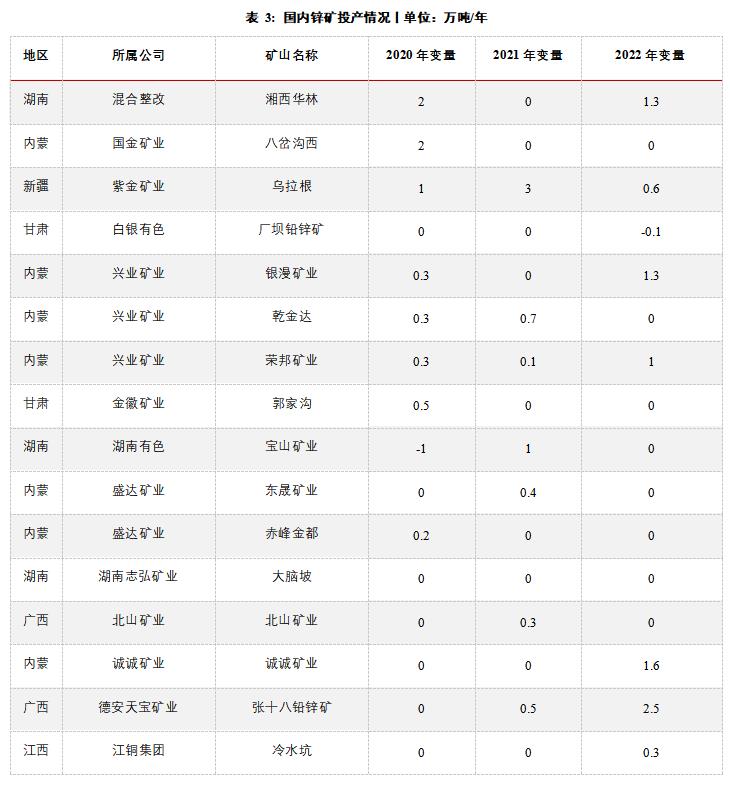
In the first half of the year, the overall supply of domestic ore was tight. On the one hand, the overall supply of domestic mines declined due to the staged interference of the Winter Olympics, the two sessions, the shortage of auxiliary materials such as explosives, and the epidemic situation in many places. According to SMM data, the domestic zinc concentrate output from January to May totaled 1.32 million tons, down 3.5% year-on-year. Since the beginning of the year, the processing fee of domestic zinc concentrate has also dropped to 3,400 yuan/metal ton, which is the lowest in recent years. On the other hand, due to the lower Shanghai-Shanghai exchange rate and the expansion of import losses, domestic smelters are weak in purchasing imported ores, which also aggravates the shortage of domestic ores. According to customs data, from January to May 2022, the cumulative import of zinc concentrate reached 1,523,986,000 (physical tons), a cumulative year-on-year decrease of 7.38%.
At present, although mining enterprises are relatively willing to produce under the incentive of higher profits, from the new production plan, there are basically no large-scale new projects in domestic mines in the second half of the year, and objective factors such as epidemic situation still exist. In addition, the grade of some domestic mines has declined, and it is expected that the supply of domestic mines will remain tight in the second half of the year. In terms of imported ore, it is expected that with the recovery of internal and external ratio, the loss of raw material import will gradually narrow, and the willingness of domestic smelters to use imported ore will be enhanced, which will supplement the domestic raw material supply. However, considering that the output of most large overseas mining enterprises in the first quarter showed a downward trend year-on-year, the amount of new minerals added overseas during the year may be less than expected. It is expected that the replenishment of imported minerals in China will be relatively limited in the second half of the year, and the supply of raw materials will remain tight.
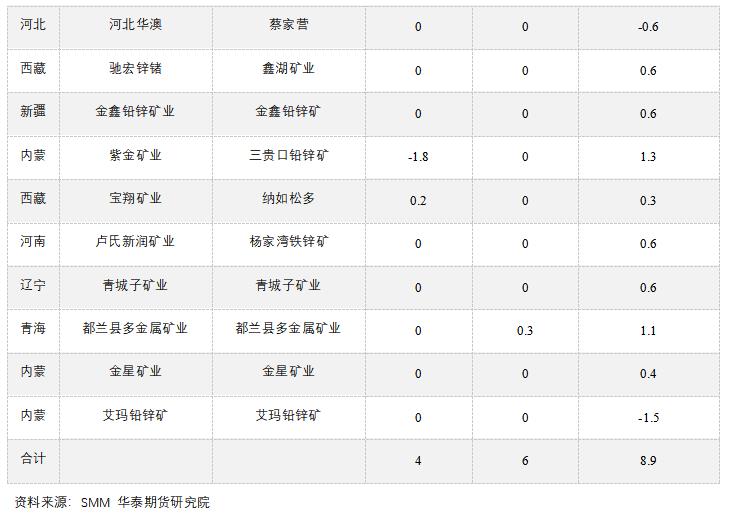
(C) High fluctuations in energy prices pay attention to overseas zinc smelting and production.
Since the fourth quarter of last year, the continuous reduction of production in European smelters affected by high-cost electricity prices has led to a decline in global zinc production. Although at the end of March, Nyrstar announced that its Auby zinc smelter in France would resume the production capacity of zinc smelting in April, it only controlled its production and operation within the scope of the French government’s electricity price subsidy. In addition, spot premiums in Europe and North America rose to record highs in the first half of the year. In Europe, the demand for galvanized steel in the construction and renewable energy industries has increased, and although Russia’s contribution to the market outside China is less than 1% in zinc concentrate and zinc ingot, the Russian-Ukrainian conflict has had an impact on the electricity cost of European zinc smelters, and European zinc smelters have maintained a reduction in production, leading to an increase in the price premium of zinc metal in this region. North America, on the other hand, was mainly affected by logistics and the closure of a zinc smelter in Canada, which led to a decline in metal production and affected metal supply. Therefore, on the whole, the supply of overseas refined zinc was tight in the first half of the year.
In the previous heating season, the energy logic promoted the zinc price to rise obviously. As we enter a new heating season in October, it is expected that supply uncertainty will persist and the demand side will rise again. At that time, the contradiction between supply and demand will intensify or drive European energy back to high volatility. The profit of zinc smelter is under pressure again, and the risk of production reduction increases. It is necessary to continue to pay attention to the trend of energy prices in Europe and whether Glencore and Nyrstar, which frequently cut production in the last heating season, will cut production again.
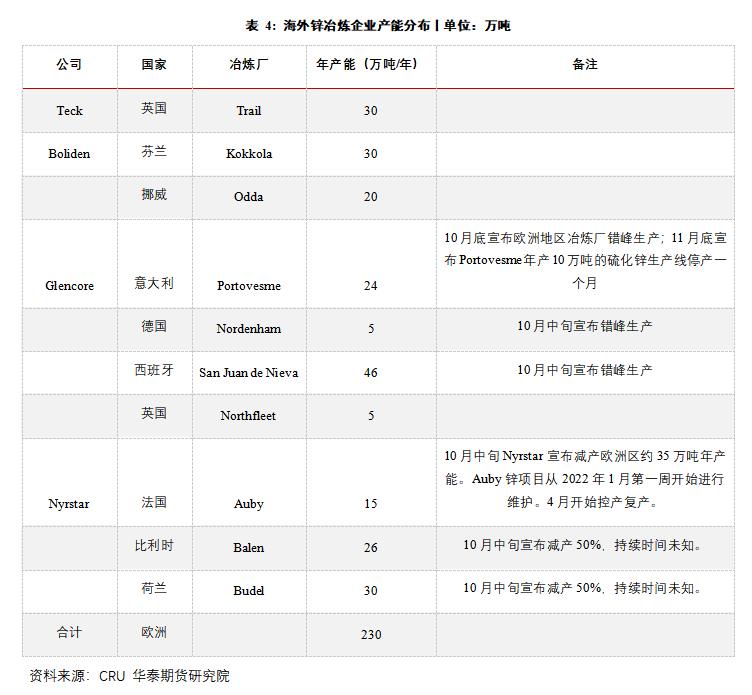
(D) Domestic zinc ingot production remained low.
According to SMM, from January to May 2022, the cumulative output of refined zinc was 2.483 million tons, a cumulative year-on-year decrease of 1.09%, and the output of refined zinc continued to be lower than market expectations. Although the price of sulfuric acid remained at a high level in the first half of the year, the by-product income supplemented part of the profit of the smelter, but considering the cost increase caused by the double control of energy consumption and load reduction, the production profit of the main zinc ingot in the refinery was basically at a loss. In addition, since the output of mines at home and abroad has been less than expected this year, the shortage of raw materials makes it difficult to increase the output of zinc ingots significantly. In the second half of the year, the bottleneck of domestic refined zinc supply still lies in the raw material end and cost. In addition, some refineries in Guangxi stopped production due to heavy rain in late June, and the expected output remained relatively low.
In terms of import and export, according to the General Administration of Customs, China imported 47,000 tons of refined zinc from January to May, compared with 231,000 tons in the same period last year, and exported 54,000 tons of refined zinc, while only 30,000 tons were exported in the same period last year. In the first five months, refined zinc turned into a net export of 7,000 tons, compared with a net import of 229,000 tons in the same period last year. The main reason is that the capacity of European smelting end is limited, and the low Shanghai-Shanghai ratio in the first half of the year keeps the import window closed, while the export window was once opened, and domestic refined zinc exports supplement overseas supply. With the gradual restoration of the Hulun ratio in the second half of the year, it is expected that the import of zinc ingots will improve month on month.
Fourth, the consumer side
(A) the recovery of the primary processing end is slow.
The epidemic situation in COVID-19 has had a great impact on all aspects of the zinc industry chain, mainly focusing on the supply and transportation of raw materials and the consumption of finished products downstream. Judging from the downstream consumption of zinc in the first half of the year, the East China market with Shanghai as the center and the North China market with Tianjin as the center have been hit by epidemic in different degrees since March. The processing enterprises are affected by factors such as rising raw material prices, blocked transportation and rising freight rates, and their start-up performance is relatively low, and the peak consumption season has not been fulfilled. Since mid-May, with the improvement of the epidemic situation and the initial confirmation of the resumption of production in Shanghai, the start-up of processing enterprises has recovered slightly, but some export orders are still lost.
Judging from the situation at the primary processing end, it is expected that zinc plating will start in the second half of the year or be boosted by the terminal infrastructure, while zinc alloy and zinc oxide will be flat.
Galvanizing started to rebound slightly.
The start of galvanizing industry has rebounded slightly recently, but it has not yet recovered to the same level as last year. On the one hand, due to the global economic downturn, the overall demand in overseas markets has weakened, and overseas enterprises have gradually resumed work and production, and domestic export orders have weakened. On the other hand, under the impact of the domestic epidemic, the data of the real estate and automobile industries are sluggish and domestic demand is insufficient.
Although it is difficult to solve the dilemma of the construction industry in a short period of time, and zinc plating is mostly used in the post-real estate cycle, it is expected that the real estate sector will drive the consumption of zinc plating relatively dull. However, infrastructure projects may bring more demand for zinc plating, and we can expect infrastructure to drive consumption of zinc plating.
Zinc alloy orders are relatively optimistic.
After the epidemic, the overall recovery of zinc alloy market is limited. Although the epidemic situation in East China has improved since late May, the operating rate of some zinc alloy factories has rebounded slightly, but the terminal orders of alloy enterprises such as doors, windows, kitchens, furniture and hardware have not fully recovered, which has dragged down the demand for zinc alloy.
However, with the steady growth of domestic demand expected to improve, coupled with the recent introduction of "green home appliance subsidies" and other policies in many places in China, zinc alloy consumption will be stimulated to some extent. In addition, with the gradual recovery of the automobile industry chain, auto parts hardware may become the main growth point of alloy demand in the second half of the year.
Zinc oxide consumption is weak
Affected by the epidemic situation in many places in China, the terminal tire enterprises started to decline in the first half of the year, resulting in less orders in the zinc oxide market and average market transactions. Considering that the recovery process of the terminal tire market is relatively slow this year, there are few new orders, and most of them are delivered in the early stage. In addition, the number of days of finished product inventory in tire enterprises is high, and it is expected that the consumption of zinc oxide will be weak in the second half of the year.
(2) The export continued to slump.
According to customs data, from January to May, 2022, the total export volume of galvanized sheet in China was 3,655,600 tons, and the total import volume was 636,300 tons. From January to May, 2022, the net export volume was 3,019,200 tons, with a cumulative year-on-year decrease of 16.51 percentage points.
In the first half of the year, the Russian-Ukrainian conflict, soaring energy costs, high inflation and other factors accelerated the Fed’s tightening of liquidity. The manufacturing PMI of major economies such as the United States, Japan and Europe all peaked and overseas demand weakened. In addition, with the gradual liberalization of epidemic prevention and control measures in Southeast Asian countries, the manufacturing industry continues to pick up, and due to the continuation of labor advantages in Southeast Asia, there is a certain outflow pressure on the initial and downstream orders such as zinc plating and die-casting zinc alloys in China. Therefore, it is expected that the export demand of zinc primary processed products will continue to be sluggish in the second half of the year.
(C) Pay attention to the development of terminal infrastructure under the policy of steady growth
Marginal recovery of real estate sector in the second half of the year
Affected by the epidemic, this year’s real estate data showed a downward trend. According to statistics, from January to May, 2022, the national land purchase area was only 23.89 million square meters, a sharp drop of 45.65% year-on-year. The year-on-year decline has continued at more than 40% this year, which is the same as last month, both of which are historical lows. From January to May 2022, the newly started housing area in China was 516.28 million square meters, down 30.56% year-on-year, and the decline continued to expand, increasing by 4 percentage points over the previous month; The completed area was 233.62 million square meters, down nearly 15.30% year-on-year, expanding again from last month. The national housing construction area was 8,315.25 million square meters, a year-on-year decline of 1 percentage point. From January to May, 2022, the sales area of commercial housing in China was 507.38 million square meters, down 23.57% year-on-year, of which the residential sales area accounted for 85%, down 28.13% year-on-year, and it continued to show negative growth this year. From January to May, the sales amount of commercial housing was 4,833.7 billion yuan, down 31.47% year-on-year, and the sales amount of residential housing was 4,231.7 billion yuan, down 34.46% year-on-year, both of which continued to expand compared with last month.
On the other hand, in the first half of this year, more than 100 cities in China successively introduced preferential policies for the real estate sector. However, in March and April, when the impact of the epidemic in China was increasing and the economic outlook was pessimistic, the preferential policies for the real estate sector began to increase. The types of preferential policies were expanded from the previous focus on provident fund, housing subsidies and talent attraction to the cancellation of the purchase restriction/sale policy, tax incentives, the use of financial instruments and strengthening the protection of rental housing construction. Since the beginning of June, it has been obvious that the sales area of commercial housing in 30 cities has started to rise rapidly, which has exceeded 820,000 square meters by the end of June, a sharp increase of 66% compared with last month, indicating that the strength of various favorable policies for real estate may be gradually increasing.
Generally speaking, although the performance of the real estate sector was depressed in the first half of the year due to epidemic factors, it can also be seen from the monitoring of relatively high frequency that the demand may gradually pick up, and it is expected that the real estate sector will pick up marginally in the second half of the year. The demand for zinc in real estate during the construction process is mainly galvanized building materials. After the completion of real estate, there is a large demand for zinc alloy pipes, all kinds of hardware, galvanized steel, air-conditioning refrigerators and other household appliances. It is expected that the demand for zinc in the real estate sector will improve in the second half of the year.
Infrastructure is an important driving force to stimulate zinc consumption.
According to the data of the National Bureau of Statistics, infrastructure investment (excluding electricity) increased by 6.7% from January to May 2022, and infrastructure investment (including electricity) increased by 8.2%. In terms of project commencement, in May 2022, 6,896 projects were started all over the country, with a total investment of 2,846.5 billion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 21%. From January to May 2022, the investment in major projects was 31,761.9 billion yuan, up 11.8% year-on-year. In terms of project volume, from January to May, the National Development and Reform Commission approved a total of 48 fixed assets investment projects with a total investment of 654.2 billion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 215.1%, a record high, which also reflected the country’s willingness to stabilize investment. Judging from the situation of projects in previous years, most projects usually land in 4-5 months, so it is expected that the huge projects approved by the National Development and Reform Commission in the first five months will land in the late third quarter, further stimulating the growth rate of infrastructure.
With the gradual easing of the epidemic situation in East China, which is dominated by Shanghai, the impact of the epidemic situation on the start of projects in various places is also gradually weakening. Considering the current downward pressure on the economy, in the absence of obvious improvement in real estate, it is expected that infrastructure will also increase its strength in the second half of the year to ensure the stable operation of the economy. Therefore, the infrastructure sector, as the sector with the largest proportion of zinc terminal consumption, is still highly resilient and is an important driving force for stimulating zinc consumption throughout the year.
Restorative growth of automobile sector
In terms of automobiles, although the sales trend in December last year was basically continued in January, the sales volume of passenger cars reached 2.262 million. However, in February, some areas were affected by the epidemic, and cities such as Jilin Province began to close cities to control the epidemic, which led to the interruption of the automobile supply chain. After that, there was a cluster epidemic in many places in China, and the international geopolitical instability increased, which affected the production and operation activities of automobile enterprises to some extent. At the same time, the rising prices of raw materials such as power batteries have pushed up the production costs of enterprises and affected the sales in the terminal market. In April, China’s automobile production and sales reached a monthly low of 1.205 million and 1.181 million respectively, down 46.2% and 47.1% from the previous month and 46.1% and 47.6% from the same period last year. However, with the improvement of the epidemic situation and the guarantee of transportation faced by policies since late April, automobile enterprises in Jiangsu, Zhejiang and Shanghai have resumed production to varying degrees, and the operating rate has steadily rebounded. According to the data of China Automobile Association, in May 2022, China’s automobile production and sales reached 1.926 million and 1.862 million respectively, up 59.7% and 57.6% from the previous month and down 5.7% and 12.6% from the same period last year. From January to May, the cumulative production and sales of 9.618 million vehicles and 9.555 million vehicles decreased by 9.6% and 12.2% year-on-year, showing obvious recovery growth. Among them, the cumulative number of new energy vehicles exceeds 2 million. It is expected that in the second half of the year, the consumption of zinc will still be boosted.
Household appliances are dull.
In terms of household appliances, according to statistics, the output of household refrigerators (household freezers) in China from January to May 2022 was 34.01 million units, down 8.1% from the same period of last year, and the growth rate was 37.3 percentage points lower than that of the same period of last year. According to CIEDATA import and export statistics, from January to May 2022, the number of refrigerators exported in China was 26.49 million units, down 12.0% year-on-year. From January to May, 2022, the national household washing machine output was 34.717 million units, down 4.1% year-on-year. In May, the production of household air conditioners was 15,544,500 units, a year-on-year increase of 0.54%; Exports reached 6.252 million units, down 11.98% year-on-year. Household appliances are expected to have "retaliatory consumption" in the short term. However, with the weakening of the epidemic, the economic order has returned to normal, and the consumption stimulus policy is superimposed, it is expected to achieve a certain degree of consumption recovery in the second half of the year. If the international market is eased with the cost of shipping and raw materials, and the demand for domestic air-conditioning products with high quality and low price will increase under the background of global inflation, the downward trend of exports will change slightly.
V. Inventory
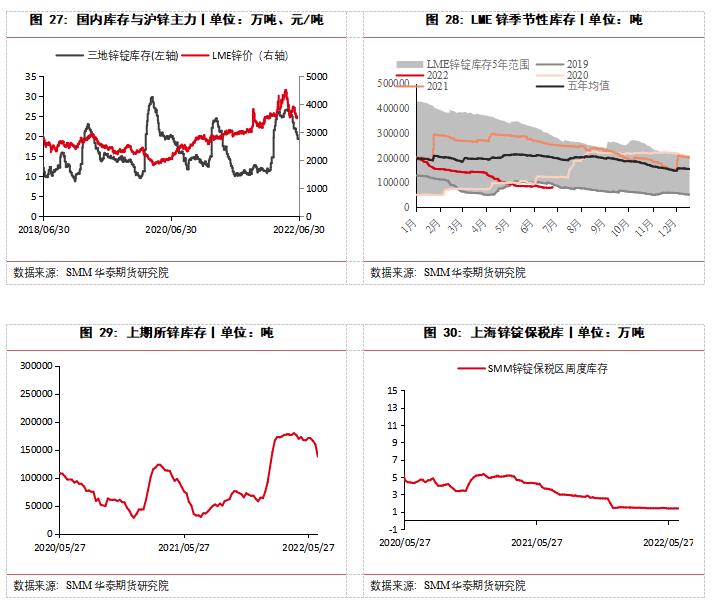
(1) It is expected that the domestic inventory will continue to be depleted.
As of June 27th, the domestic stock of zinc ingots in seven places was 197,400 tons, an increase of 66,400 tons compared with 131,000 tons at the beginning of the year. Since the Spring Festival, due to the weak downstream consumption performance, zinc ingot inventory has been at a high level. After the May Day holiday, due to the holiday and epidemic situation, many places suffered from poor transportation and poor downstream procurement. At one time, the social inventory in seven places in China increased by 281,100 tons. Since mid-May, the epidemic situation has been gradually effectively controlled, and the problem of poor transportation in many places in the early stage has been alleviated. In addition, the downstream procurement has increased slightly due to the callback of zinc prices, and the social inventory has continued to decline. Under the expectation that Shanghai and other places will resume work and resume production, and the consumption of medium and long-term infrastructure will improve, it is expected that the domestic social inventory will continue to be depleted in the second half of the year.
(B) LME inventory decline concerns the risk of crowding under low inventory.
As of June 29th, LME zinc delivery inventory was 81,075 tons, which was 118,250 tons lower than 199,325 tons at the beginning of the year. The reduction rate has slowed down since May, but the overall inventory is at a low level since April 2020. Mainly affected by factors such as the continuous reduction of production in overseas smelters, LME inventories have continued to decline this year as a whole, with LME inventories in Europe and America at relatively low levels in the same period. Therefore, we need to be alert to the risks brought by low inventory.
[Disclaimer] This article only represents the views of the third party and does not represent the position of Hexun. Investors should operate accordingly, at their own risk.
关于作者